lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm | pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm echo lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm The words aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm sound very similar, but they are two different conditions. An aneurysm is a weak spot in a blood vessel that has started to stretch .
$40.00
0 · pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm echo
1 · pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm
2 · pseudoaneurysm risk factors
3 · left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm
4 · Lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm echo
5 · Lv aneurysm post mi
6 · Lv aneurysm on echo
7 · Lv aneurysm anticoagulation
$49.99
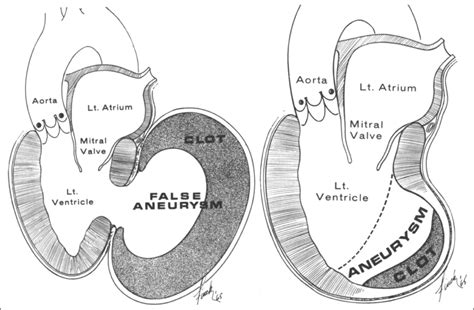
True aneurysm of LV is an area of thinned myocardium that is dyskinetic and involves the full thickness of the wall. Whereas a pseudoaneurysm of LV is a result of rupture of the ventricular free wall but contained by the overlying adherent pericardium or scar tissue.[3,4]
chanel soleil tan de chanel bronzing makeup base brush
Left ventricular aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm are a mechanical complications of MI that p.Left ventricular false aneurysm is a rare complication of myocardial rupture contained by no. Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the .
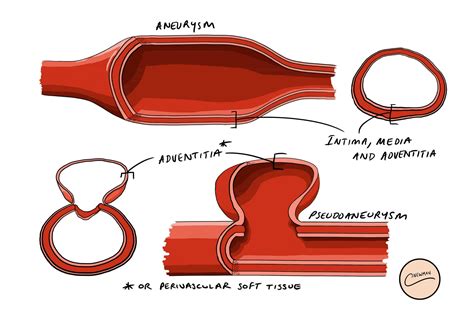
pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm echo
Left ventricular aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm are a mechanical complications of MI that pose a problem of management. The surgical indication is difficult to carry and the operative result is . The words aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm sound very similar, but they are two different conditions. An aneurysm is a weak spot in a blood vessel that has started to stretch .
Left ventricular false aneurysm is a rare complication of myocardial rupture contained by non-myocardial tissue. The most common cause of a false aneurysm is a transmural myocardial infarction, but it can also . Left ventricular aneurysms are discrete, dyskinetic areas of the left ventricular wall with a broad neck (as opposed to left ventricular pseudoaneurysms), thus often termed true . False ventricular aneurysm (pseudoaneurysm): Damage to the ventricular wall allows blood to collect in the pericardium. This membrane surrounds the heart. How common . Differentiation between LV pseudoaneurysms and true aneurysms can be challenging and investigations include transthoracic echocardiography/transoesophageal echocardiography, LV angiography, .
pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm
pseudoaneurysm risk factors
The high spatial resolution and superb tissue characterization of cardiac MRI make it ideal for evaluation of pseudoaneurysm of the left or right ventricles and for distinguishing pseudoaneurysm from true aneurysms.
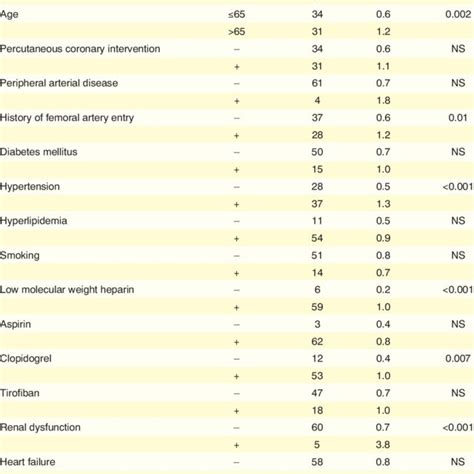
In a systematic literature review of 290 patients, MI (55%), surgery (33%), and trauma (7%) were the top 3 associations. 1 LVPs carry a substantial risk of rupture, which is considerably higher than that of a true aneurysm. .
Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the .
Patients with ICM may develop an LV aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm, which require specific management. The diagnosis and management of patients with an LV aneurysm are discussed . Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the . Pseudoaneurysm (false aneurysm) represents a collection of blood and connective tissue outside the aortic wall, the result of a contained aortic rupture, which may be due to one .Left ventricular aneurysms (LVAs) and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or serious morbidity. An LVA is most commonly the result .
Visceral artery aneurysms (VAAs) and visceral artery pseudoaneurysms (VAPAs) are defined as those affecting the celiac, superior, or inferior mesenteric arteries and their . Any arterial site used for arterial puncture can develop a pseudoaneurysm, but IPA secondary to femoral arterial access for percutaneous-based diagnostic and interventional .
Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal . In most cases, thrombus is located within or adjacent to the LV apex but can also occur with large basal inferolateral infarctions/aneurysms. Contact of blood with the fibrous .
left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm
Lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm echo
$72.00
lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm|pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm echo