lv syndrome | left ventricular hypertrophy leg pain lv syndrome Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles .
EDC LAS VEGAS 2024 LIVESTREAM. 🔴 EDC Las Vegas '24 Livestream Night 1 - kineticFIELD. Watch on. 0:00 / 0:00.
0 · lower left ventricular valve
1 · left ventricular hypertrophy weight loss
2 · left ventricular hypertrophy leg pain
3 · left ventricular hypertrophy images
CP Electronics PRM Switching Compact IP40 Ceiling Flush Mounted PIR Presence/Absence Detector Volt Free Contact. Compare. Add to project list. CP ELECTRONICS Presence Detector. REF. EBDSPIR-AD-LV.
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left .Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) happens when the left ventricle has pieces of muscle that extend into the chamber. See symptoms for LVNC.
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized .

Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) is a rare congenital heart problem. It develops from faulty development of your left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main heart.Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC): symptoms, diagnosis, and management options. Join our support group for guidance and information.
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles . The prognosis of left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) remains elusive despite its recognition as a clinical entity for >30 years. We sought to identify clinical and imaging .
lower left ventricular valve
An enlarged or thickened heart — a condition doctors call left-ventricular (LV) hypertrophy — can lead to heart failure. It also may double the risk of dementia and cognitive .
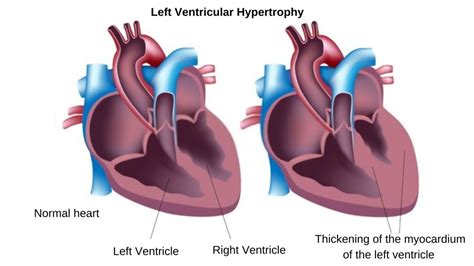
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer. Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery.
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick.
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) happens when the left ventricle has pieces of muscle that extend into the chamber. See symptoms for LVNC.
left ventricular hypertrophy weight loss
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3].
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) is a rare congenital heart problem. It develops from faulty development of your left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main heart.Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC): symptoms, diagnosis, and management options. Join our support group for guidance and information.
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles published on LVNC has grown dramatically over the past decade. The prognosis of left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) remains elusive despite its recognition as a clinical entity for >30 years. We sought to identify clinical and imaging characteristics and risk factors for mortality in patients with LVNC.
An enlarged or thickened heart — a condition doctors call left-ventricular (LV) hypertrophy — can lead to heart failure. It also may double the risk of dementia and cognitive impairment . Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer.
Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery.Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick.Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) happens when the left ventricle has pieces of muscle that extend into the chamber. See symptoms for LVNC. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3].
left ventricular hypertrophy leg pain
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) is a rare congenital heart problem. It develops from faulty development of your left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main heart.Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC): symptoms, diagnosis, and management options. Join our support group for guidance and information.
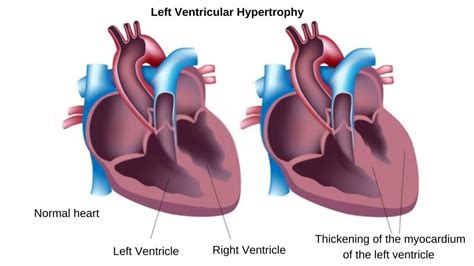
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles published on LVNC has grown dramatically over the past decade. The prognosis of left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) remains elusive despite its recognition as a clinical entity for >30 years. We sought to identify clinical and imaging characteristics and risk factors for mortality in patients with LVNC.
louis vuitton bag with flag
louis vuitton bag house of fraser
Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view.
lv syndrome|left ventricular hypertrophy leg pain